In my latest post, I have covered how to supplement a VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC deployment with Amazon FSxTM for NetApp ONTAP.
In this blog post, I am going to present the similar option delivered by VMware called Cloud Flex Storage.

Overview of Cloud Flex Storage
Cloud Flex Storage is a natively integrated cloud storage service for VMware Cloud on AWS that is entirely delivered, managed and maintain by VMware.
The solution delivers a performant, scalable, natively integrated and cost effective solution for VMware Cloud on AWS use cases where storage and compute scaling need to be independent.
Firstly, it uses a native cloud storage solution that has been developed and delivered for years with robust capability and that relies on a scale-out immutable log structured filesystem. Secondly, it is the same technology that backs VMware Cloud Disaster Recovery.
In term of consumption model, customers can consume the service on-demand or through a 1-year or 3-years subscription with a minimum charge of 25 TiB per filesystem. Secondly they can add storage capacity in 1 TiB increments to a subscription. Pricing includes production support.
Architecture model of Flex Storage
Architecturally, VMware Flex Storage is providing a standard NFS Datastore to SDDC Clusters for production workloads.
This scale-out datastore file system consists of a two-tier design model that enables to scale storage performance and capacity independently. The first tier is using NVMe disks that seats in front to offer an optimized large read cache tier. Backend controller nodes in HA Pair are supplementing the NVMe cache. The front end cache serves all reads and can deliver up to 300K IOPS per datastore (this is the peak read IOPS with at least 4 hosts).
The second tier comprises a Cloud Object Storage function based on Amazon S3 for low-cost object storage that seats behind the scene to provide elastic capacity.

You can deploy up to six Flex Storage datastores allowing for up to 2.4 petabytes of storage capacity in a single region. A maximum limit of (1) datastore can be presented to a single SDDC. That datastore can be connected to all clusters in the SDDC after being created.
You can independently provision up to ~400 TiB of usable storage capacity per datastore to VMware Cloud on AWS hosts. Moreover, the storage capacity is highly redundant across multiple AZs and is presented as an NFS datastore to the clusters. A single datastore can support up to 1000 powered on VMDKs. For current limits, it’s always preferable to check the configuration maximum Tool here.
Since version 1.22 of VMware Cloud on AWS each client can leverage multiple TCP/IP connection to NFS datastore with the support of nConnect in NFS v3. These connections are used on a round-robin basis and allow each vSphere host to increase the per datastore throughput (up to 1 GB/s).
Most importantly, any application can use transparently each Flex Storage datastore which are automatically mounted as an NFS datastore.
What kind of Workloads can benefits from Flex? Storage
In the version 1.0 of the service, Cloud Flex Storage is targeting the capacity heavy workloads where the performance needs are not as extreme as what a standard vSAN datastore can offer.
So it’s probably not recommended to use it for the highest transactional Databases but any tier 2 apps will benefits from it. When I say Tier 2, I mean lesser than mission critical system and also with lesser performance than Tier 1.
This includes for example:
- Virtualized file servers
- Backup Repositories
- Database archives
- Data warehouses
- Powered off VMs
It is important to note that a single Virtual Machine can leverage both VSAN and Flex Storage for storage needs.
Data you copy on Flex Storage is encrypted at rest and you can use the same data protection tools used for vSAN based storage like VMware SRM or vCDR (there are certain limitations in topologies supported). Customers can have both Flex Storage and vCDR services in the same organization as long as the deployments are in different regions.
When doing cloud migration with HCX, it’s recommended to first land the VMs into the VSAN datastore and move them to Flex Storage NFS datastore afterwards.
In term of region support, the service is currently available in 17 different regions across Americas, Europe, Africa, and Asia Pacific including the following:

The current list of supported regions can be found here.
What are the benefits of Cloud Flex Storage?
The solution offers multiple benefits:
- Scalability and Elasticity: it offers to scale the storage capacity on-demand without having to deploy an additional host.
- Simplified operations: it can be deployed and use through the CSP console and it is natively integrated in the VMware Cloud on AWS service.
- Optimized Costs: the service is using a simple pricing model based on $/GiB consumed and it offers a discount for commitment. There are no extra costs for things like transit or caching the data.
Deployment Process of Flex Storage
In order to deploy Flex Storage, first of all you need to ask for access to the service. Once you have access to the Flex Storage service you will have to chose a purchase option : on-demand, 1-year or 3-years subscription.
When you create a subscription, you will choose a subscription Region. It is best to select a region that covers the region where you have deployed SDDCs. Prior to activating a Region make sure the region you activate is the location where VMware Cloud Flex Storage is deployed and where you want to create datastores.
Create an IP Token
Next thing to do is to create an API token to authorize your organization’s access to the service.
For that you need first to login to the Cloud Service Portal and Select MyAccount> API Tokens. Generate a new token with the relevant privileges. Make sure the user that is creating the Token has Org owner role.
The API Token must meet the following requirements:
- Org owner role
- VMware Cloud on AWS roles: Administrator and NSX Cloud Admin
- at least one VMware Cloud Flex storage role
Once you have created the API Token you must add it to the Cloud Flex Storage UI.
Create a datastore
In order to create a new datastore you have to login to the Cloud Service Portal and Select Cloud Flex Storage tile.

From the left menu, Select Summary, and Click on CREATE DATASTORE.

Select the SDDC where you want to mount the datastore. You can select only the SDDCs that exists in the same region where the datastore was created. In my case, I have an SDDC with an already existing datastore so I can’t create a new one.

In the Create Datastore dialog box, you will pick the SDDC where you want to attach the datastore. The datastore will be created in the same AZ as the selected SDDC.
Next you have to give a name to your datastore and confirm you will be charged for the minimum 25 TiB of capacity. Launch the creation by typing CREATE DATASTORE.
Mounting the datastore in VMware Cloud on AWS
You can mount a datastore to a Cluster in VMware Cloud on AWS from the Cloud Flex Storage UI.
From the left navigation, select Datastores, and pick the datastore you want to mount.
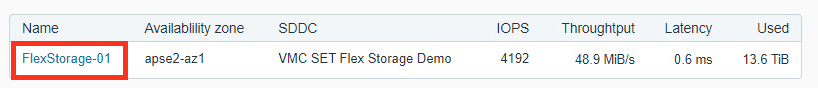
From the Actions menu, Select Mount to Cluster.

Select a cluster and Click OK.
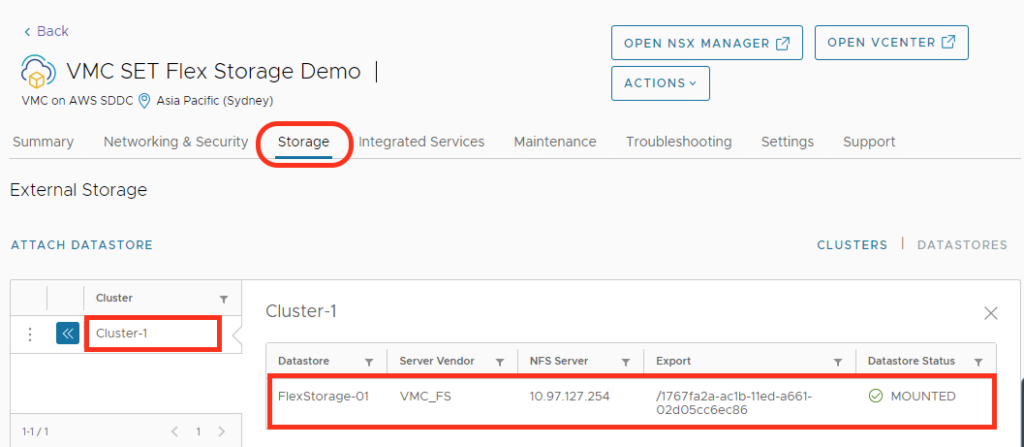
You can check the details of your datastore in VMware Cloud on AWD SDDCs from the VMware Cloud console. Select your datastore, and then click the Open in VMware Cloud button.

in VMware Cloud on AWS, select the Storage tab for the SDDC and then select the Datastores sub-tab.
Conclusion
Flex Storage is a managed service that provides NFS external storage to VMware Cloud on AWS. It provides the ability to scale storage separately than by adding host to the SDDC. By providing external NFS storage it is now possible to scale storage independently from compute and memory. With the VMware Cloud Flex storage solution, VMware can provide up to 400TiB of usable capacity per datastore.
Cloud Flex Storage is not a new technology as it is based on the same technology that has been used for VMware Cloud Disaster Recovery.
The scale out file datastore consists of a very large cacher tier for best performance with HA controllers to provide high availability, non destructive upgrade and offer 99,9% SLA, and object storage for elastic capacity at low cost.
Flex storage offers a very nice option to scale storage independently from compute with a solution that is easy to deploy and use.
One thought on “Leveraging NFS Storage in VMware Cloud on AWS – Part 2 (Flex Storage)”